Urgency-aware Routing in Single Origin-destination Itineraries through Artificial Currencies
Updated:
Tags: artificial currencies, karma, mobility, routing
Short abstract
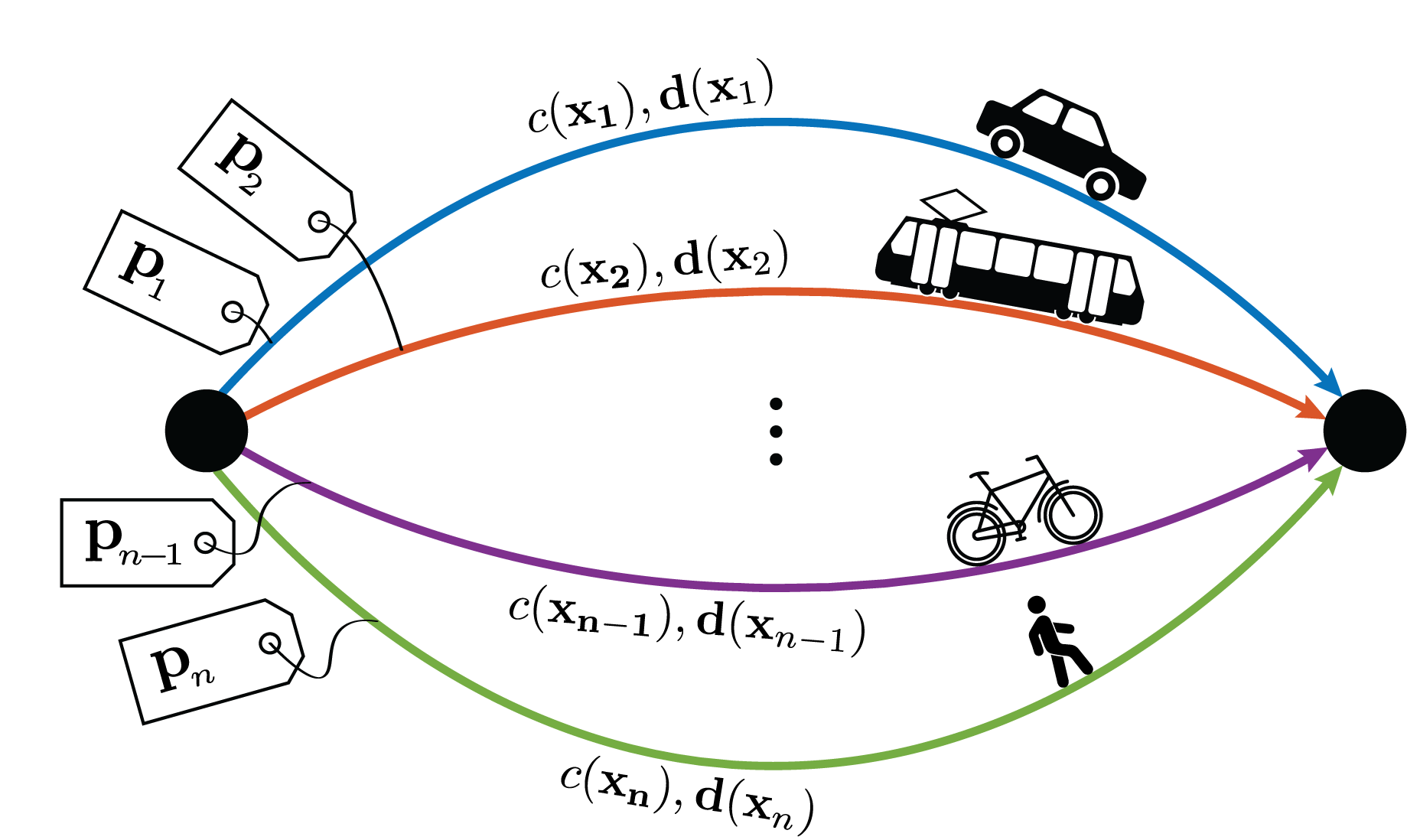
Within mobility systems, the presence of self-interested users can lead to aggregate routing patterns that are far from the societal optimum. We design a fair incentive mechanism so that the selfish behavior of the users aligns with the societally-optimal aggregate routing. The proposed mechanism is based on an artificial currency that cannot be traded or bought, but is only used when traveling. Specifically, we consider a parallel-arc network with a single origin and destination node whereby each user chooses from one of the available arcs to reach their destination on a daily basis. Taking faster routes comes at a cost, whereas taking slower routes is incentivized by a reward. Our numerical simulations show that it is possible to achieve a near-optimal solution whilst significantly reducing the users’ perceived discomfort.
Source code
A MATLAB implementation of the methods and simulations presented in this paper are openly available in an open-source repository available at github.com/fish-tue/single-origin-destination-routing. The code is thoroughly commented and is easy to follow and modify.
The source code can also be downloaded directly here (2.9 MB).
See below for step-by-step instructions on how the illustrative numerical results in [1, Section V.I ] were obtained from the source code made available.
Simulation Results
Generate Illustrative Network
To generate an illustrative network use the generate_network.m script, where the parameters regarding the network ($n$,$\mathbf{d}(\mathbf{x})$, $c(\mathbf{x})$), the population ($M$, $s_{\mathrm{min}}$, $\bar{s}$, $s_{\mathrm{max}}$, $P_\mathrm{home}$, $T$) can be set.
>> generate_network
Your initial point x0 is not between bounds lb and ub; FMINCON
shifted x0 to strictly satisfy the bounds.
First-order Norm of
Iter F-count f(x) Feasibility optimality step
0 1 1.244026e+01 1.188e+00 4.389e+01
1 2 1.030693e+00 6.698e-01 7.838e+01 4.942e-01
(...)
23 25 4.304604e-01 0.000e+00 1.178e-07 2.082e-05
Local minimum found that satisfies the constraints.
Optimization completed because the objective function is non-decreasing in
feasible directions, to within the value of the optimality tolerance,
and constraints are satisfied to within the value of the constraint tolerance.
<stopping criteria details>
System opt. flows (x_star): 0.0877055 0.13087 1.73245e-07 0.305343 0.426081
System opt. disc. (d_star): 0.561107 0.594339 0.708511 0.71071 0.910614
System opt. cost: 0.43046
Compute Near-optimal Arcs’ Prices
To compute the arcs’ prices according to the method proposed in [1, Section V.I], use the n_arcs_pricing.m script.
>> n_arcs_pricing
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Diagnostic information:
Fitness function: @(p)c(n_arcs_stationary_flows(d_star,T,p',s_max,s_bar,s_min,P_go,P_home))
5 Variable(s)
5 Integer variable(s)
6 Linear inequality constraint(s)
1 Linear equality constraint(s)
Options:
CreationFcn: @CustomCreationFcn
CrossoverFcn: @crossoverlaplace
SelectionFcn: @selectiontournament
MutationFcn: @mutationpower
PopulationSize: 20
FitnessLimit: 0.43476
StallGenLimit: 3
Display: 'diagnose'
End of diagnostic information.
Best Mean Stall
Generation Func-count Penalty Penalty Generations
1 40 0.4552 1.908 0
2 57 0.4552 1.206 1
3 74 0.4552 1.451 2
4 91 0.438 1.919 0
5 108 0.438 4.085 1
6 125 0.438 1.137 2
7 142 0.438 2.273 3
Optimization terminated: average change in the penalty fitness value less than options.FunctionTolerance
and constraint violation is less than options.ConstraintTolerance.
Elapsed time is 452.616053 seconds.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Genetic alg. prices: 79 63 39 13 -45
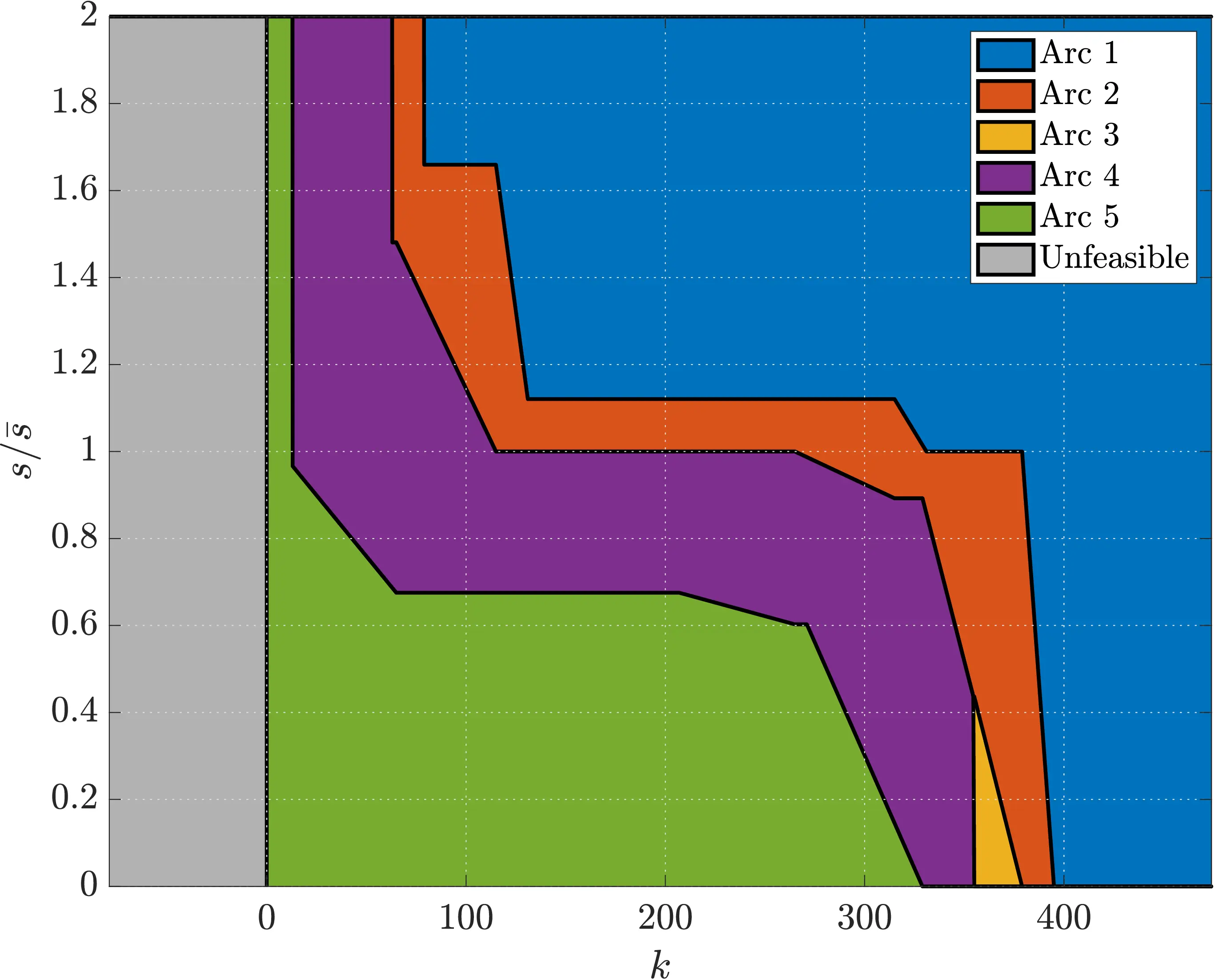
Pot Decision Landscape
The decision landscape with the selected prices at the system’s optimum can be plotted using the draw_decision_landscape.m script.
>> draw_decision_landscape.m
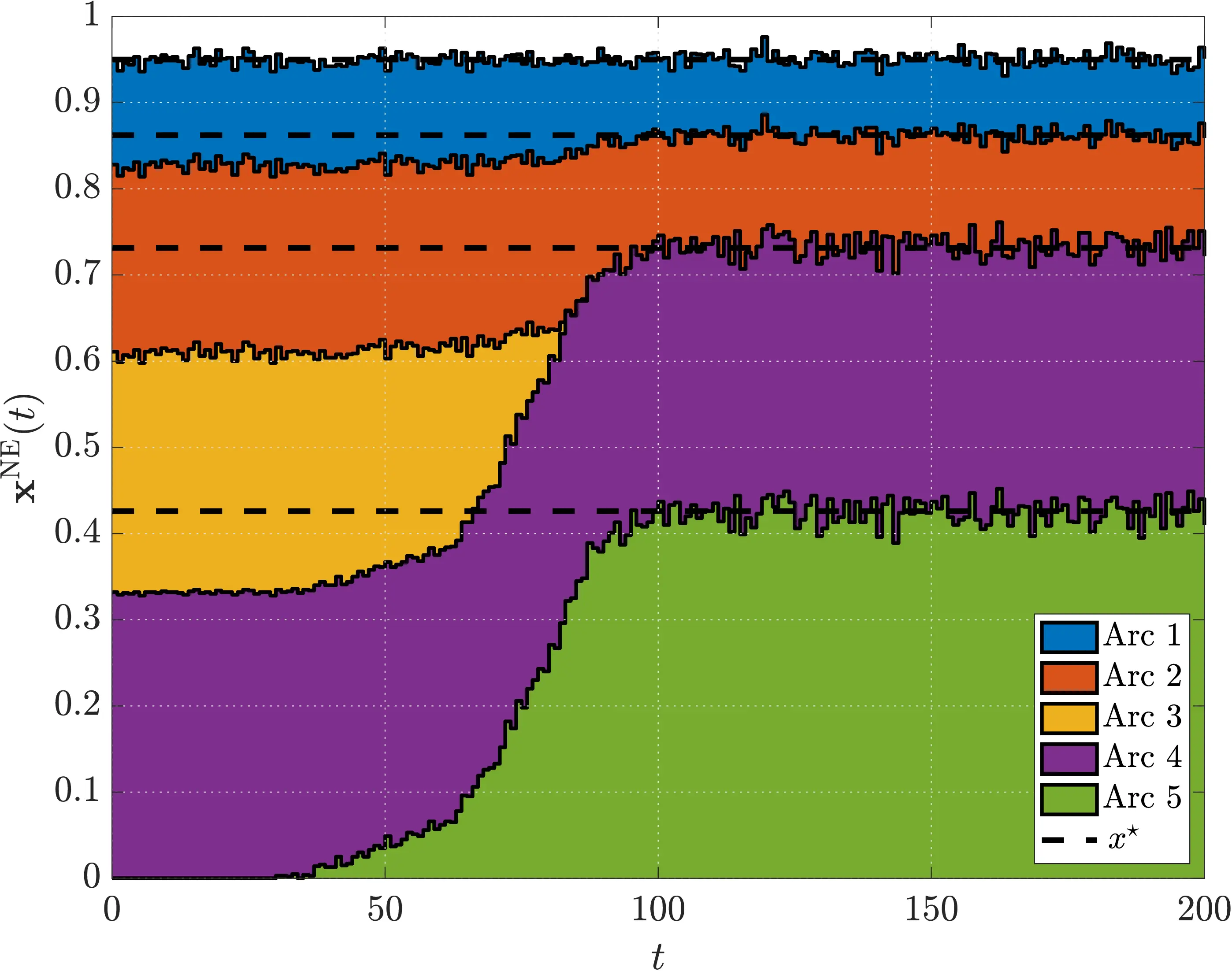
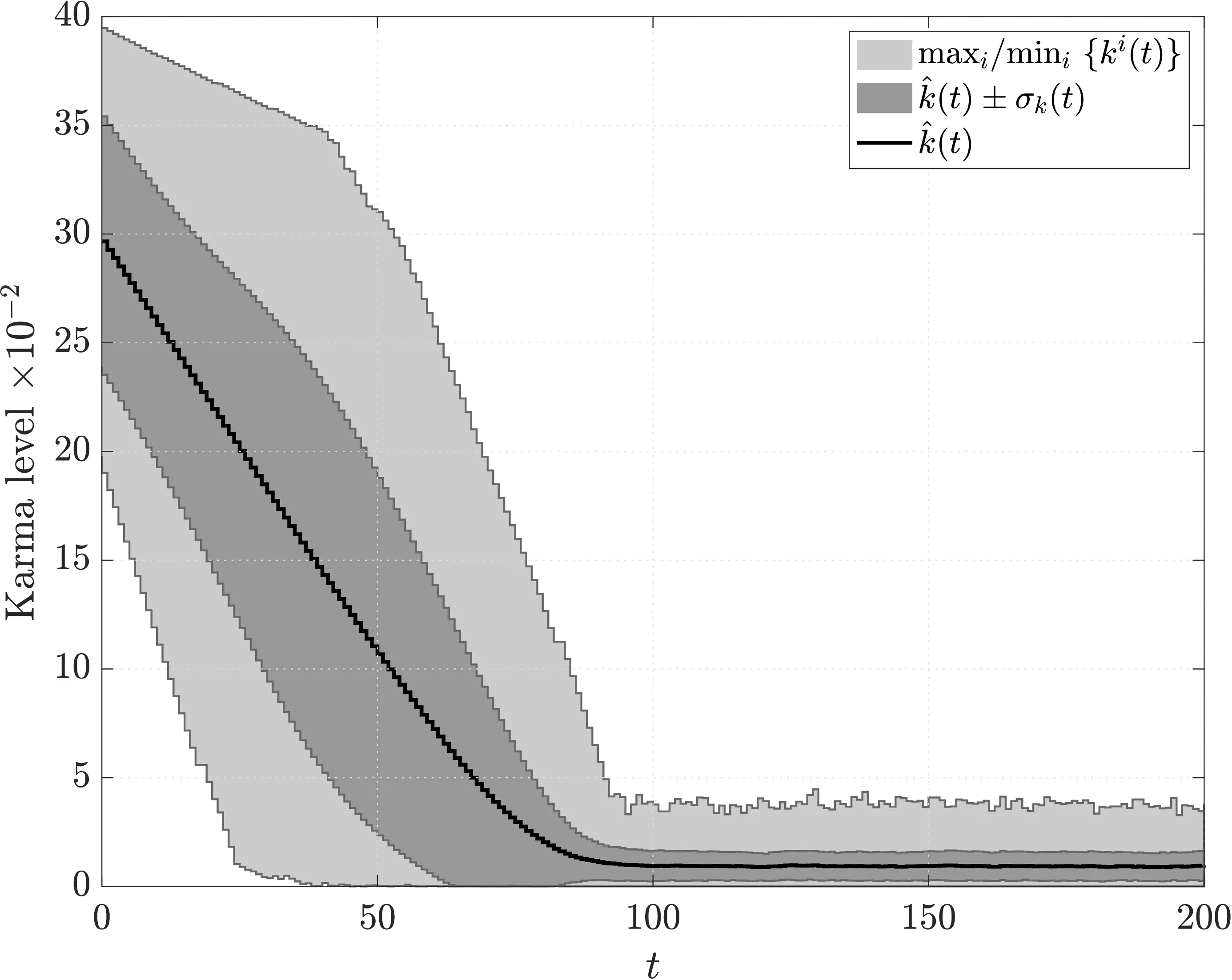
Simulate Evolution
The simulation is carried out by computing the daily Nash equilibrium and the decisions of each user. It can be carried out using the simulation.m script.
>> simulation
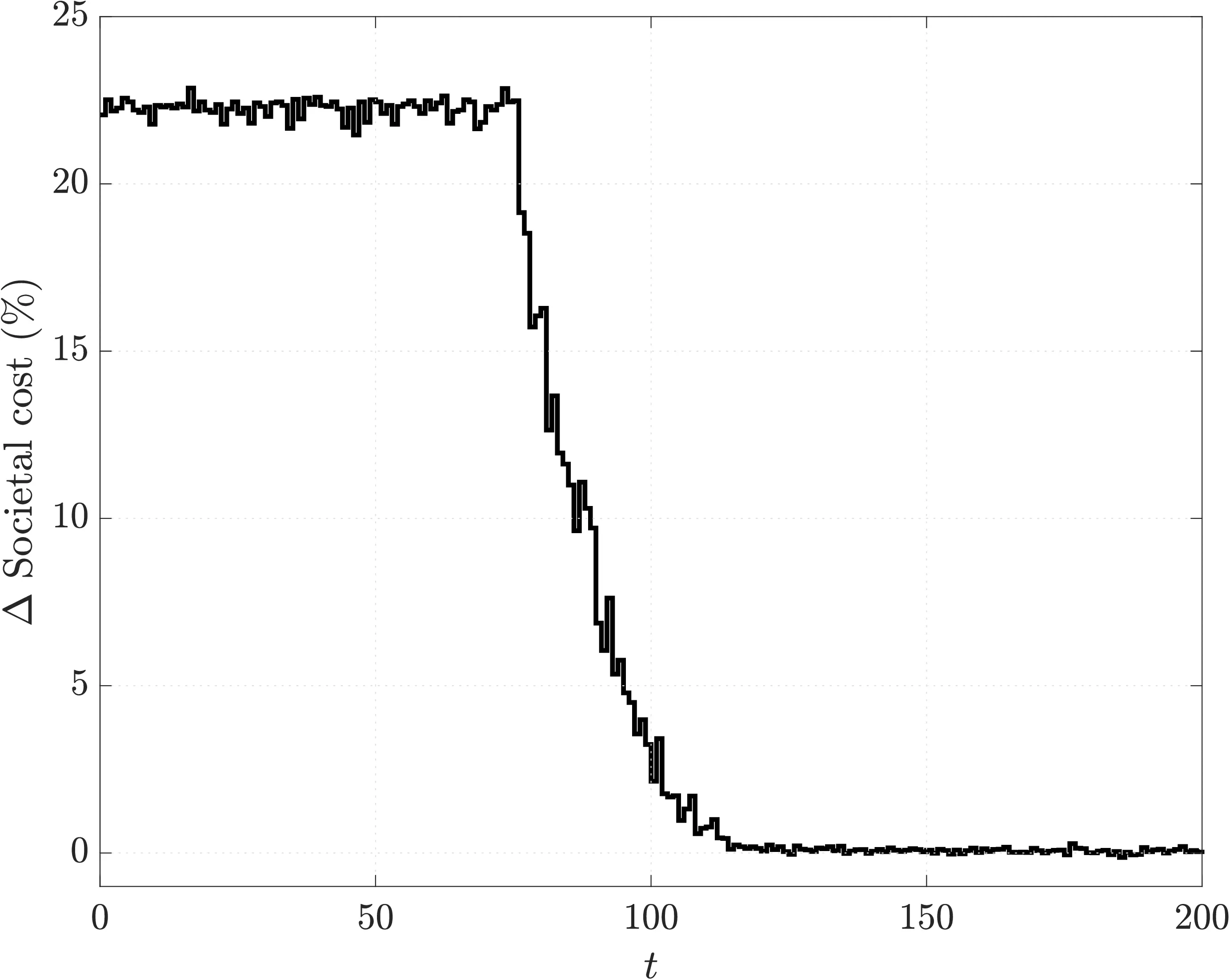
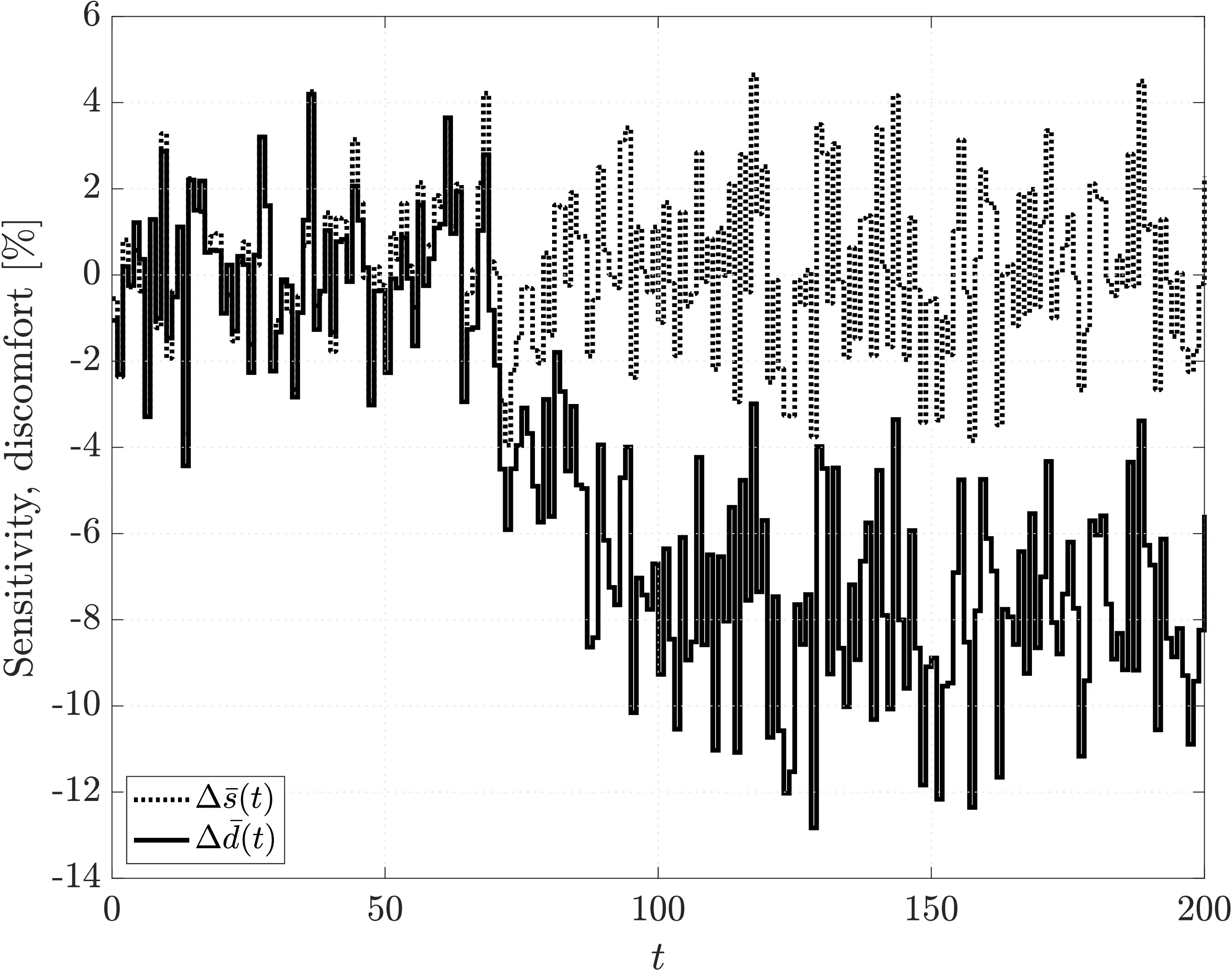
Conclusions
- When the Karma levels are very high, the users behave as if the pricing scheme were not implemented
- The system’s optimum is achieved with the selected prices
- The perceived discomfort is significantly lower in comparison to a optimal but urgency-unaware policy
Citing
If you use this repository, please reference the publication below.
L. Pedroso, W.P.M.H. Heemels, and M. Salazar, “Urgency-aware optimal routing in repeated games through artificial currencies”, 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 2023. doi:10.1109/CDC49753.2023.10383739.
@inproceedings{PedrosoHeemelsEtAl2023KarmaParallel,
author = {Leonardo Pedroso and W. P. M. H. Heemels and Mauro Salazar},
title = {Urgency-aware Routing in Single Origin-destination Itineraries through Artificial Currencies},
booktitle = {62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1109/CDC49753.2023.10383739}
}
References
[1] L. Pedroso, W.P.M.H. Heemels, and M. Salazar, “Urgency-aware optimal routing in repeated games through artificial currencies”, 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 2023. doi: 10.1109/CDC49753.2023.10383739.